On March 5, 2024, Google rolled out the March 2024 Core Update, making waves in the SEO world. This update is one of the biggest SEO events of the year, and there are plenty of reasons why. From how it’s being implemented and its connection to the Helpful Content Update, to the unique insights from Google and the current landscape of the web, this update is definitely worth paying attention to.
Let’s dive into what the March 2024 Core Update means for websites and SEOs.
The March 2024 Core Update: Summary of Events
Usually, core updates take about two weeks to roll out. However, the March 2024 Core Update was quite different—it took a full 45 days to complete!
There were numerous peaks in rank volatility as the update unfolded:
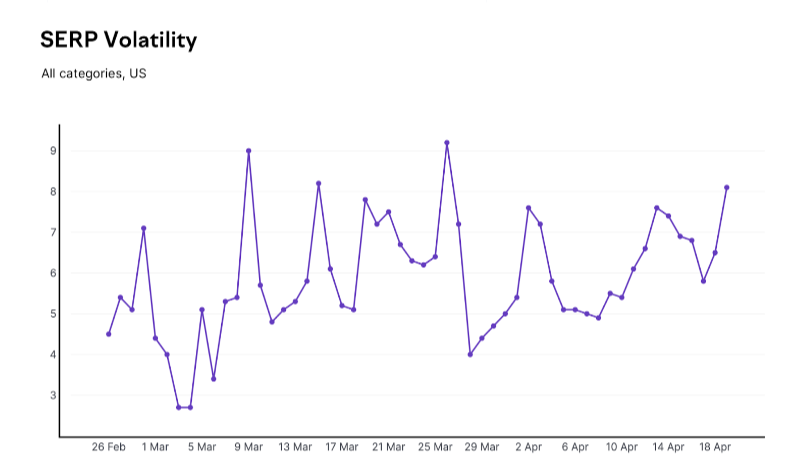
This often meant sites underwent a series of ranking reversals over the course of the update.
This left many SEOs in a state of uncertainty for almost six weeks, often wondering where their rankings would settle once the update was complete.
The extended 45-day rollout, along with the ups and downs experienced by websites and SEOs, highlights just how unique the March 2024 Core Update really was.
The Underlying Purpose of the March 2024 Core Update
The March 2024 Core Update stands out from other core updates in several ways. Typically, Google announces these updates on social media through their Search Central account or via their Search Liaison, Danny Sullivan.
For the March 2024 Core Update, they went a step further and published an entire blog post explaining the purpose of the update. Interestingly, this post wasn’t written by a Search Advocate or another visible Google employee, but by their Director of Product, Elizabeth Tucker.
To me, this shows that Google is trying to address some of the perception issues it currently faces. We’ll dive into this more later.
In her blog post, Tucker references the work started with the Helpful Content Update (HCU) in 2022, stating, “We’re bringing what we learned from that work into the March 2024 core update.”
This means that Google’s effort to find and rank “helpful” content is now a core part of their algorithm, not just a separate initiative like the HCU.
Google explained that this incorporation made the March 2024 Core Update “a more complex update than our usual core updates, involving changes to multiple core systems. It also marks an evolution in how we identify the helpfulness of content.”
Specifically, Google has moved away from relying on “one system” to determine helpfulness. Now, the core algorithm uses “a variety of signals and systems” to make that assessment.
This shift has sparked a lot of discussion within the SEO community. Personally, I believe that the new multifaceted approach to helpfulness builds on the foundation laid by the HCU. It’s not that the HCU was discarded, but rather it was improved upon and expanded.
Essentially, the current method of assessing helpfulness within Google’s algorithm is rooted in the HCU. While Google has sometimes tried to distinguish between the core algorithm and the HCU, I think they are connected, much like how the process for building a Ford Model T still influences car manufacturing today. Both processes are distinct yet fundamentally linked. That’s my take on it.
All this complexity resulted in the lengthy 45-day rollout. On April 26, we learned that the March 2024 Core Update was completed on April 19. Why was there a week’s delay in informing us? Your guess is as good as mine, and it’s just one more thing that sets the March 2024 Core Update apart from other core updates.
Google Addresses Spam Content
Another standout aspect of the March 2024 Core Update is its timing alongside several changes to Google’s spam policies. Around the same time as the March 2024 Core Update announcement, Google rolled out a spam update.
This update specifically targeted:
- Expired domain abuse
- Scaled content abuse
Regarding the latter, Google took significant action by implementing numerous manual actions.
Additionally, Google announced a new policy against “site reputation abuse” (often referred to as Parasite SEO), which would come into effect on May 5, 2024.
What Does the Update Mean for SERP?
According to Tucker, the updates to the spam policies, alongside the March 2024 Core Update, were anticipated to decrease unhelpful content on the SERP by 40%. This statement is remarkable both for the scale of the updates and the fact that Google publicly shared it. Even more surprising, after the completion of the March 2024 Core Update, Google announced that they had actually removed 45% of unhelpful results from the SERP.
This announcement comes at a time when Google is facing increased scrutiny over the quality of its organic results. Concerns have been raised about the status of small to medium publishers in the SERP, the prominence of Reddit rankings on Google, and other issues.
Google’s bold statement, “the updates led to larger quality improvements than we originally thought – you’ll now see 45% less low quality, unoriginal content in search results, versus the 40% improvement we expected across this work,” appears to be a response to the criticism suggesting that the SERP had started to stray from its original purpose.
Reviewing the Trends from the Core Update
Assessing the impact of a core update is always challenging. The extended duration of the March 2024 Core Update, coupled with its unique micro-patterns, adds another layer of complexity to this assessment
The Limitations of Traditional Metrics with the March 2024 Core Update
Relying on the traditional metrics we typically use to evaluate a core update doesn’t fully capture the essence of the March 2024 Core Update.
The nature of its rollout also makes these metrics less reliable.
For instance, let’s consider peak volatility. If we were to compare the highest points of rank volatility observed during the March 2024 Core Update with those of the November 2023 Core Update, we might conclude that the March update wasn’t particularly impactful.
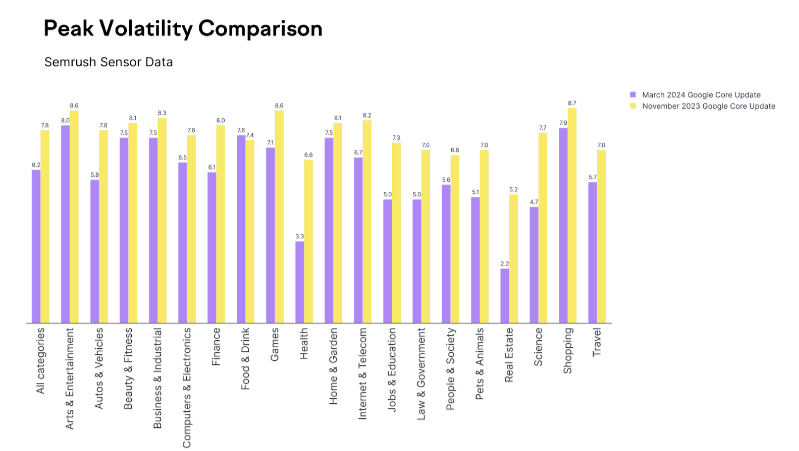
As shown above, the level of peak volatility during the November 2023 Core Update was significantly higher than that of the March 2024 Core Update across all verticals.
However, it’s important to note that comparing the peak volatility of an update that unfolds over two weeks to one that spans 45 days is not apples-to-apples. The March 2024 Core Update was characterized by its prolonged nature. It wasn’t a sudden spike in rank volatility followed by a few peaks and valleys.
The impact of the March 2024 Core Update didn’t come from a brief period of volatility. Instead, it stemmed from the extended and widespread changes in rankings over the course of 45 days. Therefore, peak volatility may not be the most relevant metric to analyze in this context.
Similarly, analyzing the change in rank volatility has its limitations. This approach compares the volatility level before the update (a period of relative calm) to a specific point of increased volatility during the update.
Comparing the rank volatility change during the March 2024 Core Update to that of the November 2023 Core Update shows no difference. Different verticals experienced varying degrees of volatility depending on the update.
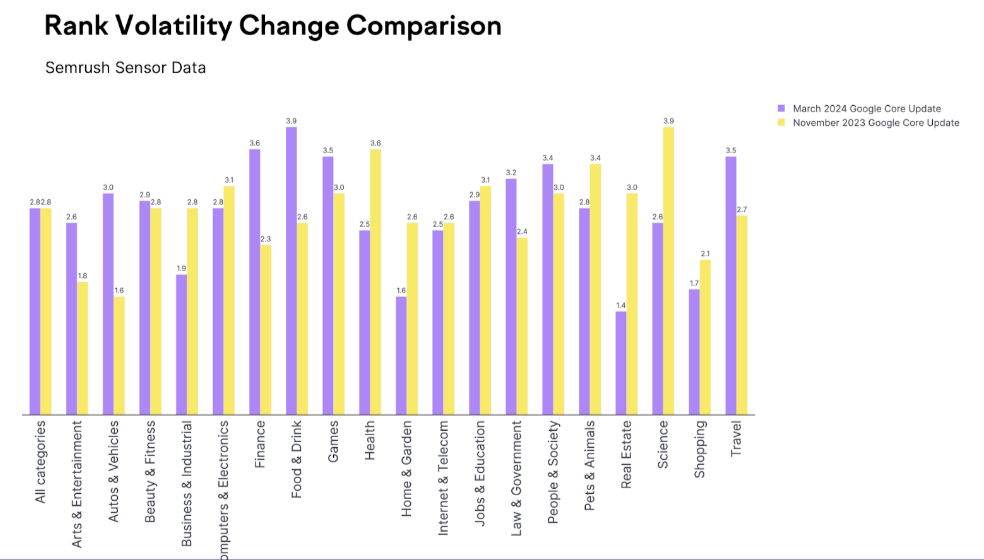
Once more, analyzing a specific moment in time for any update has its limitations, especially when dealing with an update that unfolded over 45 days. Just like relying on peak volatility, evaluating the March 2024 Core Update based on volatility change puts too much emphasis on a single moment, which doesn’t align with the prolonged nature of this update.
Why So Volatile?
To truly grasp the impact of the March 2024 Core Update, it’s crucial to delve into the nature of rank volatility.
Let’s begin by looking at the average number of positions gained or lost, which was 2.3 positions:
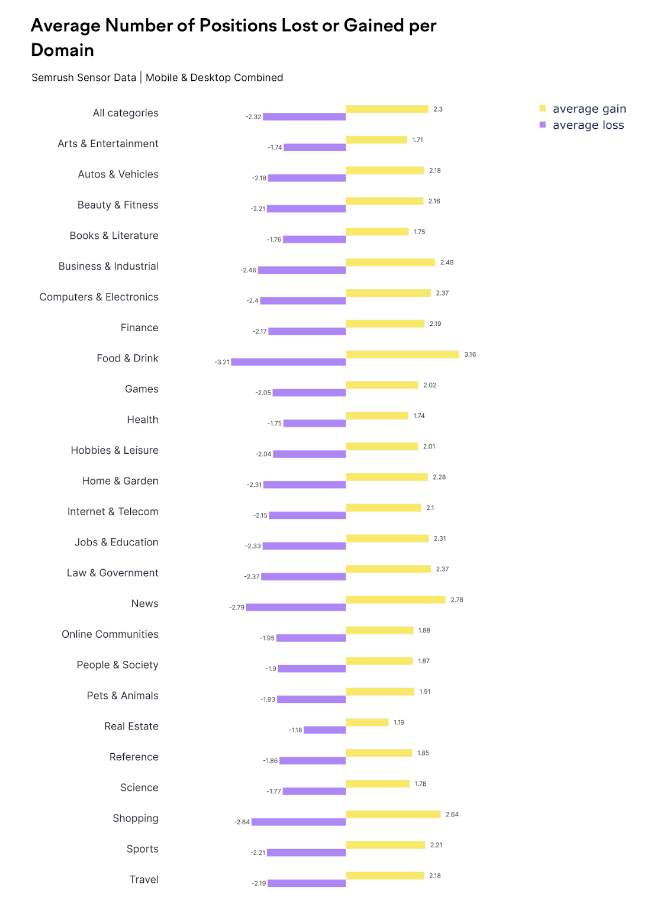
Interestingly, this is slightly lower than the average seen during the November 2023 Core Update, which was around 2.7 positions.
However, this average reflects a normalization across the web. It considers sites that experienced significant movement as well as many sites that were either unaffected or minimally affected.
To gain a deeper understanding of the March 2024 Core Update, we should look at the extent of volatility. Let’s examine how much Google felt it was under-rewarding or over-rewarding URLs and how it adjusted for that.
The data below provides a snapshot of this:
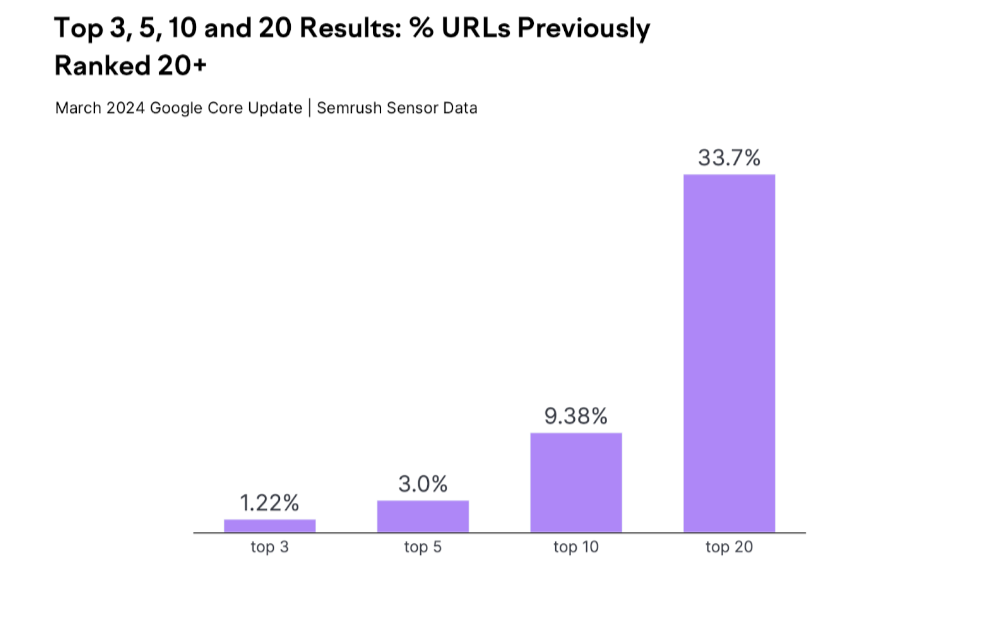
As illustrated, 9.38% of the top results post-update were not even in the top 20 prior to the March 2024 Core Update. Similarly, 3% and 1.22% of the top five and top three results respectively did not rank in the top 20 before the update.
This marks the first notable deviation from the November 2023 Core Update. The data below shows a significant increase in the percentage of URLs ranking in the top 10 during the March update, which were not in the top 20 before the update, compared to the November update:
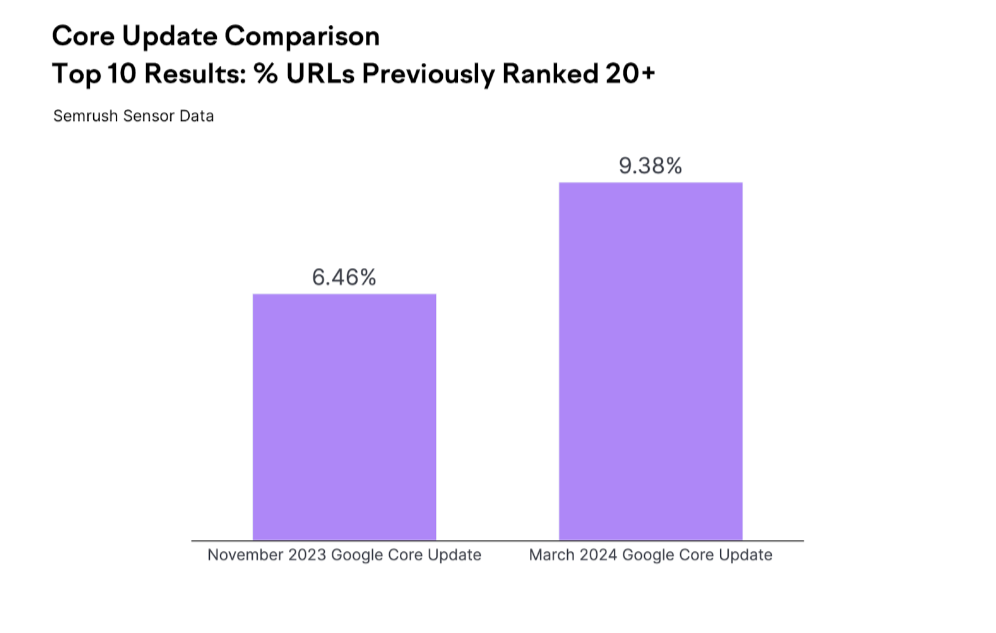
However, when comparing the November 2023 Core Update to the March 2024 Core Update at the very top of the SERP, there isn’t a significant increase in this percentage.
As shown below, the difference was less than one percentage point:
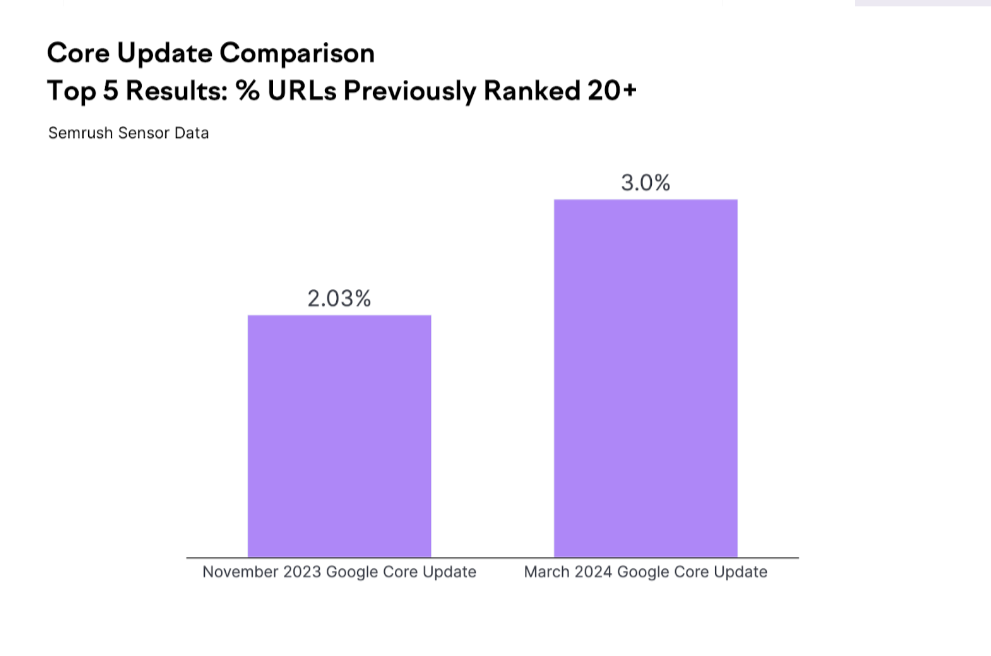
This observation aligns closely with my own qualitative analysis, where I analyzed the ranking patterns of around 300 SERPs during the update. One trend that stood out was the significant volatility within the bottom half of “page one,” while the top of the SERP remained relatively stable.
This trend is supported by the earlier data comparing the November 2023 Core Update to the March 2024 Core Update.
There’s a noticeable difference in the number of URLs ranking in the top 10 that didn’t rank in the top 20 before the update, but the difference is much smaller when looking at the top five.
Interestingly, there’s a consistent pattern when examining the increase in URLs that were outside the top 20 before the update but now rank among the top five after the March 2024 Core Update.
As shown below, the overall 1% difference between the two updates was consistent across various verticals, with only a few exceptions:
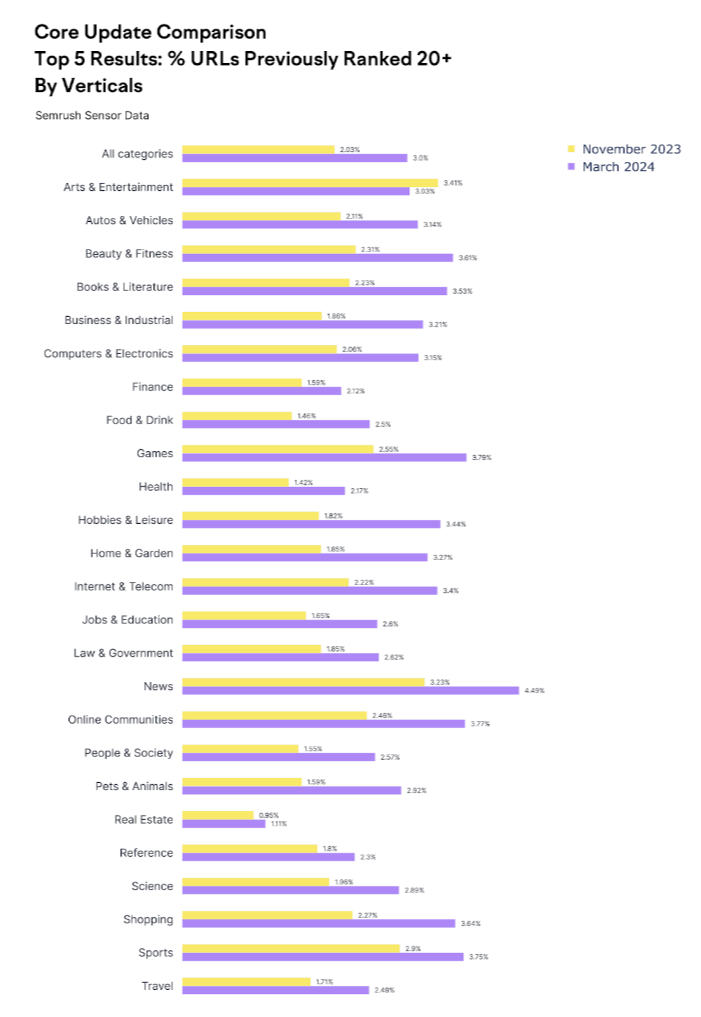
Absolutely, the data presented in this article provides valuable insights, but it’s also essential to stay connected to the ongoing changes and nuances of the update as it progresses. Combining quantitative data with a qualitative understanding of the update’s impact gives a more holistic view of the March 2024 Core Update.
Conclusion
The March 2024 Core Update by Google was a significant event in the SEO world, characterized by its 45-day rollout, which was longer than usual. Unlike previous updates, Google announced this update through a blog post by their Director of Product, Elizabeth Tucker, indicating a shift in their approach to ranking content.
One of the key changes brought by this update was the incorporation of the principles from the Helpful Content Update (HCU) directly into the core algorithm. This change aimed to improve the quality of search results and was part of Google’s efforts to address criticism regarding the quality of organic search results.
Analyzing the impact of the March 2024 Core Update was challenging due to its extended rollout and unique characteristics. Traditional metrics like peak volatility and rank volatility change were less relevant in this context, as the update’s effects were spread out over a longer period.
Despite this, data showed that the update led to a significant number of URLs ranking in the top positions that were not previously in the top 20. This trend was consistent across various verticals, indicating a universal pattern of change in search results.
Overall, the March 2024 Core Update marked a shift in Google’s approach to ranking content, with a focus on improving the quality and relevance of search results. Understanding the impact of this update requires a combination of quantitative data and qualitative analysis to fully grasp its implications for SEO.